Procedure Summary
-
-
In general, for all third-party EtherCAT
 EtherCAT is an open, high-performance Ethernet-based fieldbus system. The development goal of EtherCAT was to apply Ethernet to automation applications which require short data update times (also called cycle times) with low communication jitter (for synchronization purposes) and low hardware costs devices, use the built-in IDE
EtherCAT is an open, high-performance Ethernet-based fieldbus system. The development goal of EtherCAT was to apply Ethernet to automation applications which require short data update times (also called cycle times) with low communication jitter (for synchronization purposes) and low hardware costs devices, use the built-in IDE "Integrated development environment"
An integrated development environment is a type of computer software that assists computer programmers in developing software.
IDEs normally consist of a source code editor, a compiler and/or interpreter, build-automation tools, and a debugger features to Scan, Map Network Devices, and configure devices through the PDO Selection/Mapping, Distributed Clock, and CoE Init-Commands tabs. The Procedure Summary and Example are only applicable if the IDE cannot support a device, due to non-conformance to the EtherCAT standard or custom device specific configurations supported by a third-party configuration tool.
"Integrated development environment"
An integrated development environment is a type of computer software that assists computer programmers in developing software.
IDEs normally consist of a source code editor, a compiler and/or interpreter, build-automation tools, and a debugger features to Scan, Map Network Devices, and configure devices through the PDO Selection/Mapping, Distributed Clock, and CoE Init-Commands tabs. The Procedure Summary and Example are only applicable if the IDE cannot support a device, due to non-conformance to the EtherCAT standard or custom device specific configurations supported by a third-party configuration tool.
A summary of this procedure is as follows:
- Connect only the standard Kollmorgen drives and ATI I/O devices in the EtherCAT network. Scan the network as normal. Online Configuration of the AKD drives is possible using the embedded WB screens in the IDE
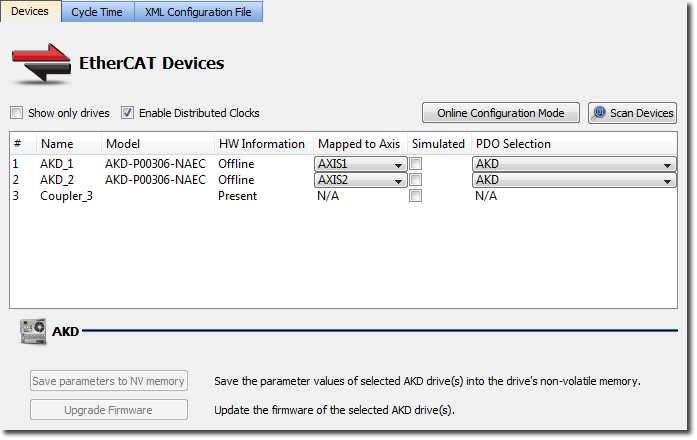
Figure 7-235: Mapping of standard components
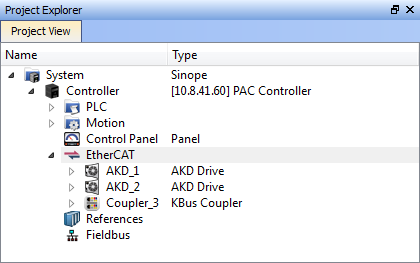
- Add the non-standard devices to the network. Use the EtherCAT Configurator as described further in this document to create the XML
 "Extensible Markup Language "
XML is a general-purpose markup language. It is classified as an extensible language because it allows its users to define their own tags file.
"Extensible Markup Language "
XML is a general-purpose markup language. It is classified as an extensible language because it allows its users to define their own tags file. - Export the .XML file from the EtherCAT Configurator and import it into the KAS project.
- IF the EtherCAT device order has changed when adding the third-party device, update the EtherCAT addresses in the KAS dictionary in order to match the final configuration.
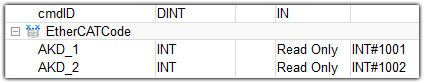
- Save the .KAS project to save the EtherCAT Configuration
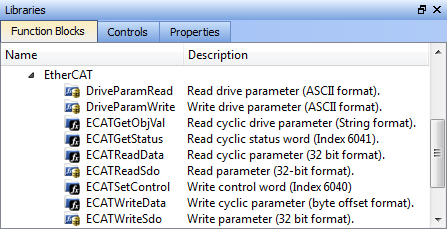
- Read and write information from the non-standard I/O device use the following EtherCAT function blocks